
Circuit Diagram
Index 1020
SWITCHING_MODE_MOTOR_SPEED_CONTROL
Published:2009/7/22 1:34:00 Author:Jessie
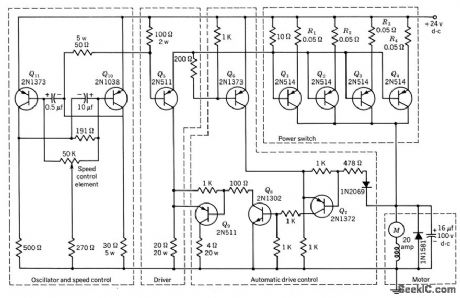
Power-switch stage consists of four 2N514 transistors in parallel, to handle starting or stalled motor current approaching 100amp.Rectifier and capacitor in parallel with motor minimize possibility of damage to power transistors when they switch off heavily inductive motor load. Variation of lime duration of on and off portions of power transistor cycle, controlled by 50K potentiometer in mvbr, provides control of motor speed while giving high staring torque.-Texas Instruments Inc., Transistor Circuit Design, McGraw-Hill, N.Y., 1963, p 477. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1237)
CONTROL_TONE_DECODER
Published:2009/7/22 1:33:00 Author:Jessie
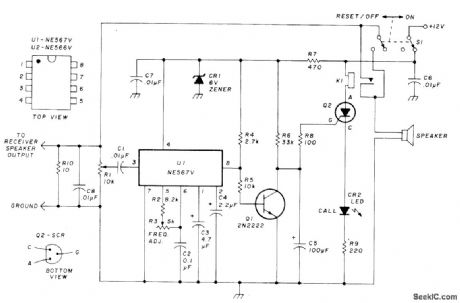
Permits monitoring local VHF FM repeater for calls from friends without having to listen to chatter of others or to repeater noise. Operation is similar to that of Motorola paging units in which special tone is transmitted to disable squelch of receiver being called. Each friend has tone encoder for his transmitter, set at correct frequency for connecting loudspeaker so desired call can be heard. Red LED comes on to confirm that loud-speaker is connected. Audio from receiver loud-speaker is fed into pin 3 of NE567V PLL U1.When correct tone frequency is received, pin 8 drops from 4V to near 0V, turning off Q1 and turning on Q2. Q2 closes relay K1, to connect loudspeaker, and holds it on until RESET switch is operated. Q2 is Radio Shack 276-1059 or other small SCR. CR1 is 1N4735, and CR2 is red LED.-K. Wyatt, Private Call System for VHF FM, Ham Radio, Sept.1977, p 2-64. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2291)
SILENT_COR
Published:2009/7/22 1:31:00 Author:Jessie
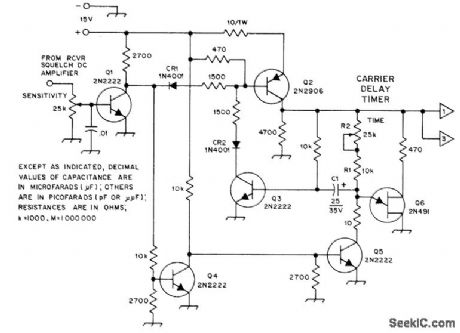
Solid-state carrier-operated relay uses Q1 to sense DC level change from receiver squelch and forward-bias Q2, thus latching Q3 on. Q4 and Q5 prevent C1 from accumulating a charge. Q6 is then disabled as long as there is an incoming signal. Q2 feeds terminals 1 and 3 for switching transmitter on and starting timer that shuts of f transmitter after 3 min of use.Q6 is timer that holds transmitter on for short time after incoming carrier has dropped out (carrier tail). B2 adjusts tail length, usually 1,-2 s.-D. L. Moon, Solid-State Repeater Control, QST, Oct. 1974, p 19-21. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2131)
REVERSING__DRIVE__FOR__SHUNT_WOUNDMOTOR
Published:2009/7/22 1:30:00 Author:Jessie
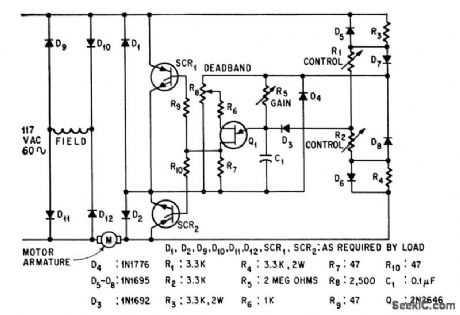
Silicon controlled recliners in Half-wave circuit act with unijunction transistor and two rheostats to adjust speed in either direction,-J. C. Hey, The Widening World of the SCR, Electronics, 37:25, p 78-85. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(789)
AF_SQUELCH
Published:2009/7/22 1:29:00 Author:Jessie
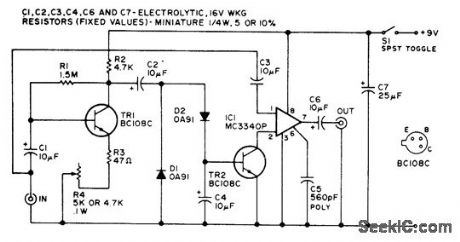
Simple audio squelch circuit suppresses all input signals below preset threshold.-Circuits, 73 Magazine, Holiday issue 1976, p 170. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2218)
TWO_SOURCE_CONTROL
Published:2009/7/22 1:29:00 Author:Jessie
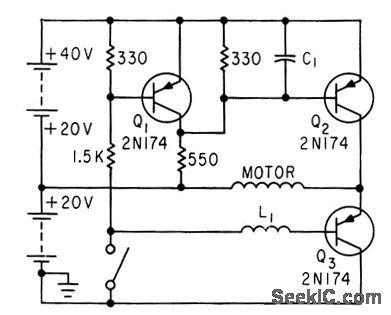
Acts as bidirectional current switch that selects one of two oppositely polarized current sources for d-c motor of gyro or accelerometer. Switch is operated by opposing forces of motor torsion and acceleration. Motor torsion opens switch, reducing speed and therefore torsion of motor, and acceleration forces then dose switch. Shaft speed is therefore proportional to acceleration.-F. W. Kear, D-C Motor Controls Improve System Accuracy, Electronics, 33:41, p 76. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(663)
TRIAC_DIAC_REVERSING_SERVO_CONTROL
Published:2009/7/22 2:02:00 Author:Jessie
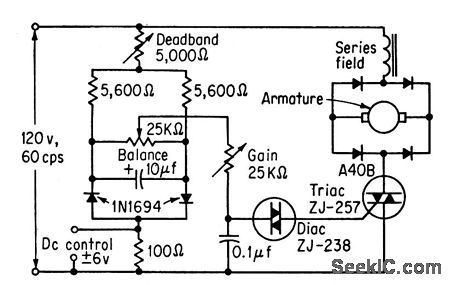
Varies speed and direction of 5-amp reversible series ac motor in accordance with d-c control signal. Polarity of control signal determines direction of rotation. Gain potentiometer adjusts slope of speed versus control voltage curve.-M. P. Southworth, Bidirectional Static Switch Simplifies Ac Control, Control Engineering, March 1964, p 75-76. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(2099)
GOVERNOR_TRANSISTOR_SPEED_REGULATOR
Published:2009/7/22 2:01:00 Author:Jessie
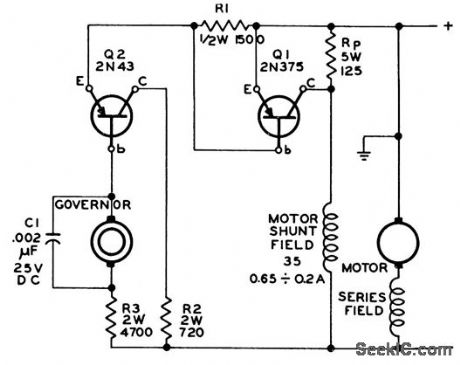
Centrifugal governor is used as error detector, with contacts handling only a few microwatts. Two-transistor amplifier actuated by governor is connected across motor field resistor, with power being obtained from 24 v d-c motor bus. Maintains 0.5-hp motor speed at 6,000 rpm over input voltage range of 20 to 30 v.-Transistorized Speed Regulator, Electronic Circuit Design Handbook, Mactier Pub. Corp., N.Y., 1965, p 30. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1219)
BALANCED_BRIDGE_REVERSING_DRIVE
Published:2009/7/22 2:00:00 Author:Jessie
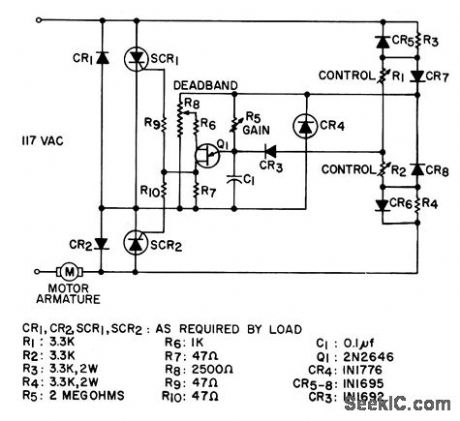
Phase-sensitive servo drive supplies reversible half-wave power to armature of small permanent magnet or to shunt motor. Power circuit consists of two half-wave circuits back-to-back (SCR1-CR1 and SCR2-CR2) fired by ujt Q1 on either positive or negative line half-cycle depending on direction of unbalance of reference bridge containing sensing element R1, which can be photoresistor, thermistor, potentiometer, or output from control amplifier.- Silicon Controlled Rectifier Manual, Third Edition, General Electric Co., 1964, p 142. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(811)
ACCELERATION_SENSING_SWITCH_WITHOUTOVERSHOOT
Published:2009/7/22 1:59:00 Author:Jessie
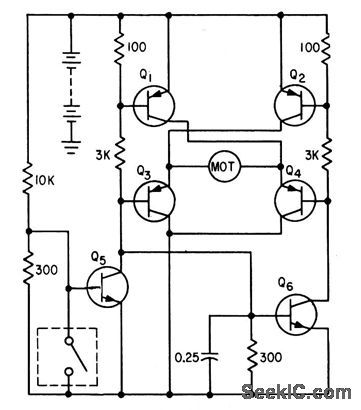
Provides null capture in indicated balance point for each level of acceleration, with bidirectional current switching for accelerometer molar.-F. W. Kear, Dynamic Fluid Switch Senses Acceleration, Electronics,34:38,p 64-67. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(758)
PUNCHED_TAPE_CONTROLS_MOTOR
Published:2009/7/22 1:58:00 Author:Jessie
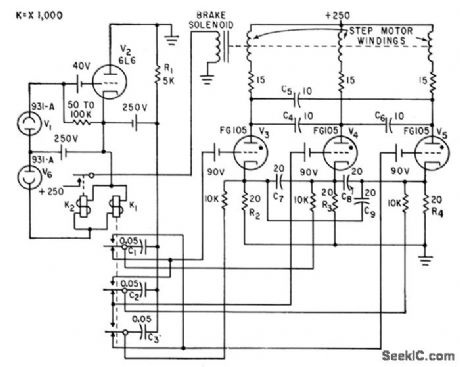
Photolubes sense holes punched in programmed tape and feed resulting command signals through relays to three thyratrons whose loads are windings of step motor for milling machine.-A. G. Thomas, Digital Control of Machine Tools, Electronics, 33:11, p 174-176. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(725)
REVERSIBLE_HALF_WAVE_SPEED_CONTROL
Published:2009/7/22 1:57:00 Author:Jessie
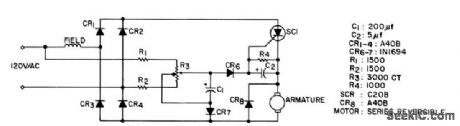
Simple circuit is adequate for majority of universal series-wound motor drive applications:Direction of ratation depends on which half-cycle scr conducts, since series fleld is in ac leg of bridge rectifier.- Silicon Controlled Rectifier Manual, Third Edition, General Electric Co., 1964, p 144. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(962)
UNIVERSAL_MOTOR_SPEED_CONTROL
Published:2009/7/22 1:55:00 Author:Jessie
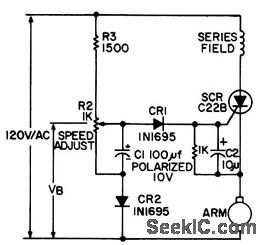
Regulated speed control is achieved by varying conduction angle of scr placed in series with armature and field of universal a-c/d-c motor. Makes use of motor residual field to induce counter emf in armature proportion to speed, +or use as feedback signal. Provides stable operation at low speeds for sewing machines and small appliances. - Silicon Controlled Rectifier Manual, Third Edition, General Electric Co., 1964, p 143. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(0)
HALF_WAVE_DRIVE_FOR_D_C_MOTOR
Published:2009/7/22 1:54:00 Author:Jessie
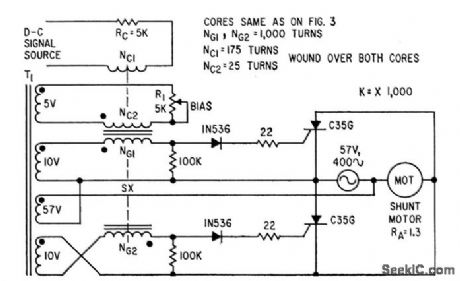
Uses controlled recliners to control armature of d-c shunt motor or d-c torquer, for applications requiring push-pull output for reversible drive. Saturable reactor control windings ore wound over both cores together. Maxi-mum current during reversal from top speed in one direction to top speed in opposite direction is approximately 20 amp, with cur rent dropping to 10 amp in 0.1 sec.-W. R. Seegmiller, Controlled Rectifiers Drive A-C and D-C Motors, Electronics, 32:46, p 73-75. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(808)
Half_wave_thyristor_control_with_average_voltage_feedback
Published:2009/7/22 1:54:00 Author:Jessie
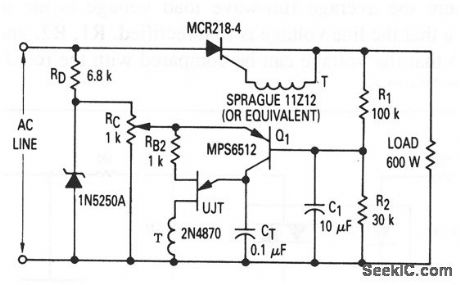
This circuit shows a UJT used as a thyristor trigger (with feedback), where the average load voltage is the desired feedback variable. R1, R2, and C1 average the load voltage so that the voltage can be compared with the set point that is determined by RC. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(814)
ULTRASONIC_CONTROL_RECEIVER
Published:2009/7/22 1:54:00 Author:Jessie
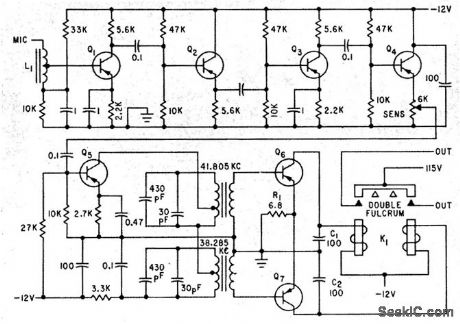
Five-stage amplifier Q1-5 amplifies both control signals, 38.285 kc and 41.805 kc, while Q6 and Q7 operate as class B detector-amplifiers to eliminate need for separate diode detectors. Desired control frequency energizes only one coil of double-fulcrum motor control relay. while noise acts on both coils and keeps relay balanced.-Transistor Amplifier Controls Remote Appliances, Electronics, 34:21, p 59.
(View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(641)
SMALL_D_C_MOTOR_CONTROL
Published:2009/7/22 1:53:00 Author:Jessie
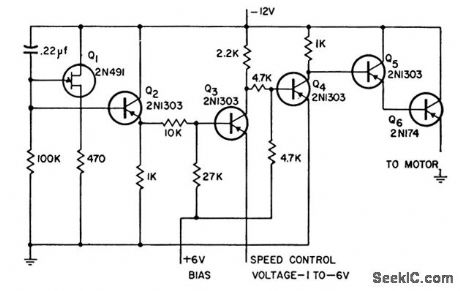
Will drive small permanent-magnet motor at speeds below 1rpm up to full speed, in direct proportion to control voltage, without friction problems. Applies full voltage of12 v to motor and provides speed regulation by interrupting voltage at about 50 cps and varying ratio of on time to off time.-Motor Speed Control, Electronic Circuit Design Handbook, Mactier Pub. Corp., N.Y., 1965, p 28. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(741)
FULL_WAVE_REVERSING_D_C_MOTOR_DRIVE
Published:2009/7/22 1:52:00 Author:Jessie
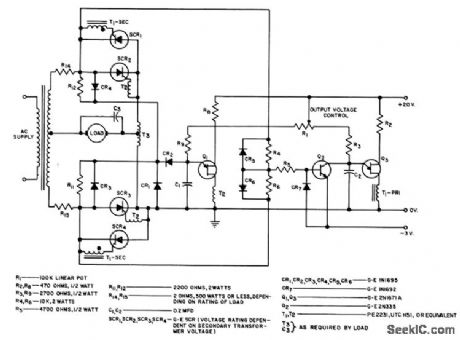
Designed around two scr's with common cathode (SCR2 and SCR3) and two more with common anodes (SCR1 and SCR4). If load is d-c motor, plugging action occurs if R1 is reversed suddenly. R14 and R15 limit fault current if voltage transient should ire odd or even-numbered pair simultaneously.- Silicon Controlled Rectifier Manual, Third Edition, General Electric Co., 1964, p 141. (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(709)
The principle circuit diagram of 915MHz intermediate power amplifier composed of RF2104
Published:2011/5/9 21:48:00 Author:May | Keyword: 915MHz, middle power, amplifier
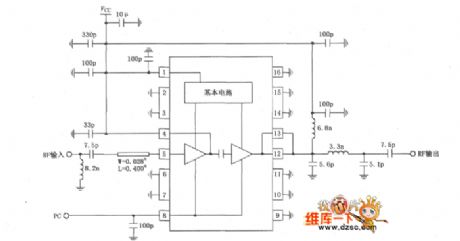
The principle circuit diagram of 915MHz intermediate power amplifier composed of RF2104 is shown in the following diagram:
(View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(763)
555_SQUARE_WAVE_GENERATOR
Published:2009/7/22 2:15:00 Author:Jessie
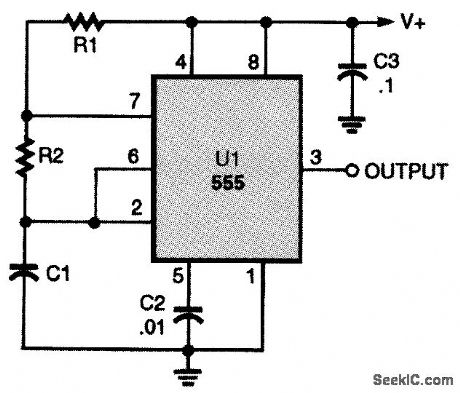
The 555 can be connected in either monostable or astable configurations, but for continuous square waves, the astable circuit is used. The square-wave signal appears at pin 3 of the 555. The out-put frequency of the 555 astable multivibrator is found from
ƒo=1.44/[(R1+2R2)C1]The duty cycle of the 555's square-wave output is determined by the relationship between R1 and R2, and is given by: Duty cycle=(R1+R2)/R2 (View)
View full Circuit Diagram | Comments | Reading(1269)
| Pages:1020/2234 At 2010011002100310041005100610071008100910101011101210131014101510161017101810191020Under 20 |
Circuit Categories
power supply circuit
Amplifier Circuit
Basic Circuit
LED and Light Circuit
Sensor Circuit
Signal Processing
Electrical Equipment Circuit
Control Circuit
Remote Control Circuit
A/D-D/A Converter Circuit
Audio Circuit
Measuring and Test Circuit
Communication Circuit
Computer-Related Circuit
555 Circuit
Automotive Circuit
Repairing Circuit